Is smoking cannabis and driving the new drinking and driving?

Alcohol consumption and smoking among Ontario students in grades 7-12 is at an all-time low; however recreational use of over-the-counter drugs is on the rise. Prescription drug misuse and driving after using drugs also remain elevated according to the 2013 Ontario Student Drug Use and Health Survey (OSDUHS) released by the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health (CAMH). The survey of 10,272 students from across Ontario is Canada's longest-running systematic study of alcohol and other drug use among youth, and one of the longest-running surveys in the world.
Over-the-counter and prescription drugs
The survey shows one in eight (representing 120,000 middle and high school students in Ontario) reported taking a prescription opioid pain medication recreationally in the last year, and the majority of these students said that they got the drugs from home. About one per cent (representing 13,500 students) reported using stimulant drugs (used to treat ADHD) without a prescription.
There was an increase in the number of students who reported using over-the-counter cough medication to "get high," with over 94,000 students (about 10%) engaging in this behaviour. This was the only drug to show an increase in recent years. One in six high school students reported symptoms of a drug use problem; this represents 132,700 students in grades 9-12.
Substance use and driving
Eighteen per cent of students reported being a passenger in a car driven by someone who had been drinking alcohol. Four per cent of students with a G-class driver's license said they had driven a vehicle within one hour of consuming two or more drinks - this is an estimated 12,700 adolescent drivers in Ontario.
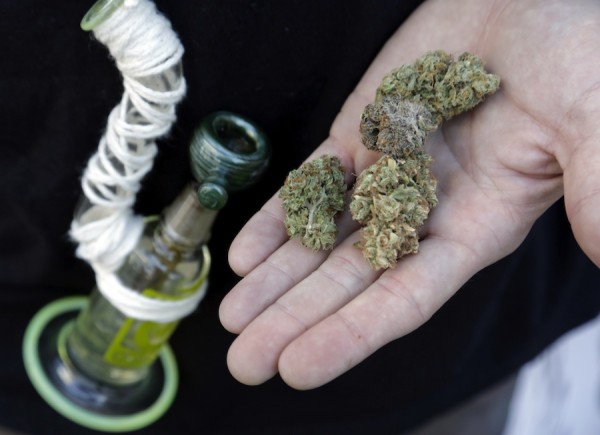
Cannabis smoking and driving levels were even higher. Despite the serious impact that smoking cannabis can have on psychomotor skills and the ability to drive safely, one in ten licensed students reported driving a car within one hour of smoking cannabis. This represents 31,500 adolescent drivers in Ontario. Fourteen per cent of students reported being a passenger in a car where the driver had been using drugs.
"The number of students who report using cannabis and driving has remained the same in recent years which tells us that students do not take the potential dangers of driving while under the influence seriously," said Dr. Robert Mann, CAMH Senior Scientist and OSDUHS Principal Investigator. "The public health messages around the dangers of drinking and driving seem to have had an impact on our youth but the same can't be said for cannabis use, which is worrisome."
Drinking
Alcohol use among Ontario students reached an all-time low with 50 per cent (representing 483,900 students) reporting drinking alcohol in the past year. "Though the overall decline shows promise, we see that the kids who are drinking are doing so in dangerous ways," added Dr. Mann. "One in five (representing 193,400 students) reports binge drinking at least once in the past month and a similar percentage report blacking out on at least one occasion when drinking alcohol in the past year. Eight per cent report being injured or injuring someone else while they had been drinking."
New this year
New in this year's OSDUHS are questions on the use of waterpipes and electronic cigarettes. Almost 10 per cent (representing 88,400 students) reported smoking tobacco through a waterpipe in the past year. About 15 per cent of high school students (representing 99,800 students) reported smoking electronic cigarettes in their lifetime. For the first time the survey asked students whether they had used synthetic cannabis, commonly known by street names, "K2" or "spice." Two per cent - representing over 17,000 students - had tried the drug.
"These new numbers give us some insight into the use of alternative and emerging drugs among young people," said Dr. Hayley Hamilton, CAMH Scientist and Co-Investigator on the OSDUHS. "We see that while cannabis use among students is holding steady since our last survey at around one quarter of students, this new synthetic form has emerged and we will want to track its prevalence in future surveys. The same holds for smoking - while the rate of students smoking has leveled off over the past few years, we see that youth are still smoking cigarettes and tobacco, but in alternate ways."
Regional differences
- Students in Toronto and Western Ontario reported the non-medical use of opioid prescription pain medication at higher rates than the rest of the province (15 per cent and 13 per cent respectively).
- Students in the north were less likely to use prescription opioid pain medication (7 per cent) but reported higher rates of hazardous drinking than the provincial average (19 per cent and 16 per cent respectively).
- Students in the east reported higher rates of hazardous drinking than the provincial average (20 per cent and 16 per cent respectively).
Dec 12, 2013 03:37 PM EST