Insulin Pumps are More Effective in Controlling Blood Glucose Levels in Diabetics: Study
Insulin pumps are better than injections in controlling blood glucose levels in diabetics, finds a study.
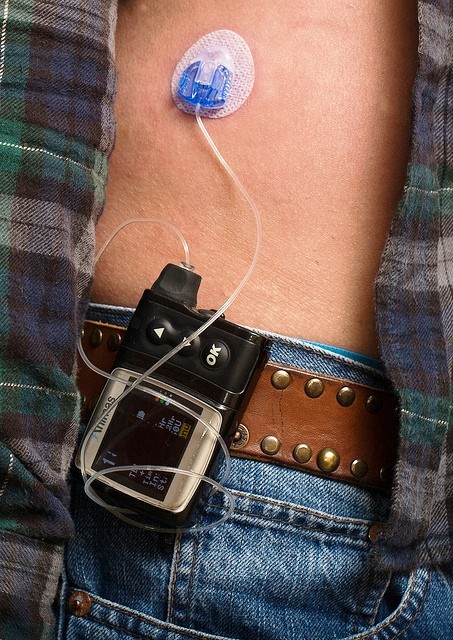
Individuals with advanced diabetes mellitus rely on insulin therapy, which involves taking insulin shots daily. Despite using medications, only one-third of the patients with diabetes are able to manage their sugar levels. Recently, researchers found insulin pumps or devices that supply certain amount of active or short-acting insulin by a catheter placed under the skin are more beneficial than taking multiple insulin injections.
The study looked at data of 495 diabetic patients aged between 30 and 75 who took insulin shots every day. Two months later the level of HbA1c or the gycolated hemoglobin, a marker of blood sugar control, in 331 participants was above the minimum target range, between eight and 12 percent. These subjects switched to OpT2mise insulin pumps and had significant reduction in average blood sugar content than those who took insulin injections for half a year. Around 55 percent of the subjects under insulin pump therapy reached the target range of HbA1c levels of 8 percent or below.
The total hours spent in hypoglycemic condition in a day was three hours lesser in those who used insulin pumps. The daily dose of insulin received was 20 percent lesser with pump therapy than taking injections.
"Pumps enhance effective insulin absorption and increase insulin sensitivity thanks to the continuous daily subcutaneous insulin delivery. Our findings open up a valuable new treatment option for those individuals failing on current injection regimens and may also provide improved convenience, reducing the burden of dose tracking and scheduling, and decreasing insulin injection omissions," said Yves Reznik, study author and professor at the University of Caen Côte de Nacre Regional Hospital Center, Caen, France, in a news release.
The authors believe that unlike conventional insulin therapy, the OpT2mise pumps are safe, cost effective and free from the hassles of monitoring the dosage level of insulin.
"Many people with type 2 diabetes work hard to maximize the benefit of multiple daily injections of insulin but still struggle to keep their blood glucose values in target range. This study supports use of an insulin pump as another safe and effective treatment option for this particular group of patients without promoting weight gain or hypoglycemia," said Virginia Peragallo-Dittko, executive director of the Diabetes and Obesity Institute at Winthrop-University Hospital in Mineola, New York, reports the Health Day News.
More information is available online in the journal 'The Lancet'.
Jul 03, 2014 06:51 AM EDT